The T score statistic, which measures the probability that an individual will develop osteoporosis in the future, can be challenging to understand for non-statisticians. The T-score compares how likely your bone density is to fall below the normal range as you age based on standard population values, and it’s used to determine whether you are at risk of developing osteoporosis or other diseases that affect bone health in older adults. Here’s how you can explain this to someone who isn’t necessarily well-versed in statistical terms.
What is a T-score?
T-score measures how far your test results are from what’s statistically expected based on data from other people who have taken the same test. If your score is at or below the mean, it’s considered normal; if it’s above the mean, it’s considered gifted. The higher your score, the more likely you are to have an IQ that will allow for high achievement later in life.
How is the t-score used?
The t-score is used to measure the difference between two groups of data. The t-score is calculated by taking the mean of one group and subtracting it from the mean of the other group, then dividing that number by the standard deviation. This number is then compared against a table (usually called an INVT table) with values for various degrees of difference, which will tell you whether or not your scores are statistically significant (enough).
A t-score has no units, so it’s just a number that falls on a scale. The bigger this number is, the more significant your results are. To calculate this value yourself using an INVT calculator online, all you need to know are your two sets of data and their respective means and standard deviations.
Why are men, on average taller than women?
The average height for men and women is strikingly different. The average American male is 1.8 inches taller than the average American female. Average size of an American man is 5’9, and the average height of an American woman is 5’4. Why is this so? Is it because men have more testosterone than women, or do they have something else that gives them their growth spurt earlier in life? The truth is, we don’t know for sure.
Some scientists believe there are differences in hormones between males and females that may help explain why males are, on average taller than females.
Statistical significance isn’t always clear cut
In the world of statistics, there are two types of statistical significance: statistical significance and clinical significance. Statistical significance is typically measured by something called the t-score or z-score. The t-score is used when comparing your results with data from a similar study, while the z-score is used when comparing your results with data from an entirely different study. For example, if you have an average weight of 180 pounds and someone else’s average of 170 pounds, these two people have significant differences in their weights. If someone has an average weight of 150 pounds and someone else has an average weight of 185 pounds, then these two people do not have significant differences in their weights because they are so close together.
The value of knowing statistical probability isn’t clear cut
It’s hard to give one answer as the value of knowing statistical probability isn’t clear-cut. For example, let’s say that I am looking at an INVT calculator, and the probability of getting heads is 50%. But what does that mean for me? Well, it could be different for two people.
If I’m flipping a coin with someone who has never flipped before, there’s a 75% chance they won’t get heads on their first try. If instead, the question was, what are my chances of winning the lottery, then it would be best to talk about probabilities with an expert statistician.
Demonstrate statistical probability to someone who isn’t an expert
The T score is used for statistical measurements. The score is derived from an INVT Calculator, which gives an individual’s statistical probability of developing various diseases. The score is calculated by taking the person’s age and multiplying it by their relative risk factor.
The result is subtracted from the average of people of the same age. A positive number means the person has a higher than average chance of getting sick, while a negative number means they have less chance.
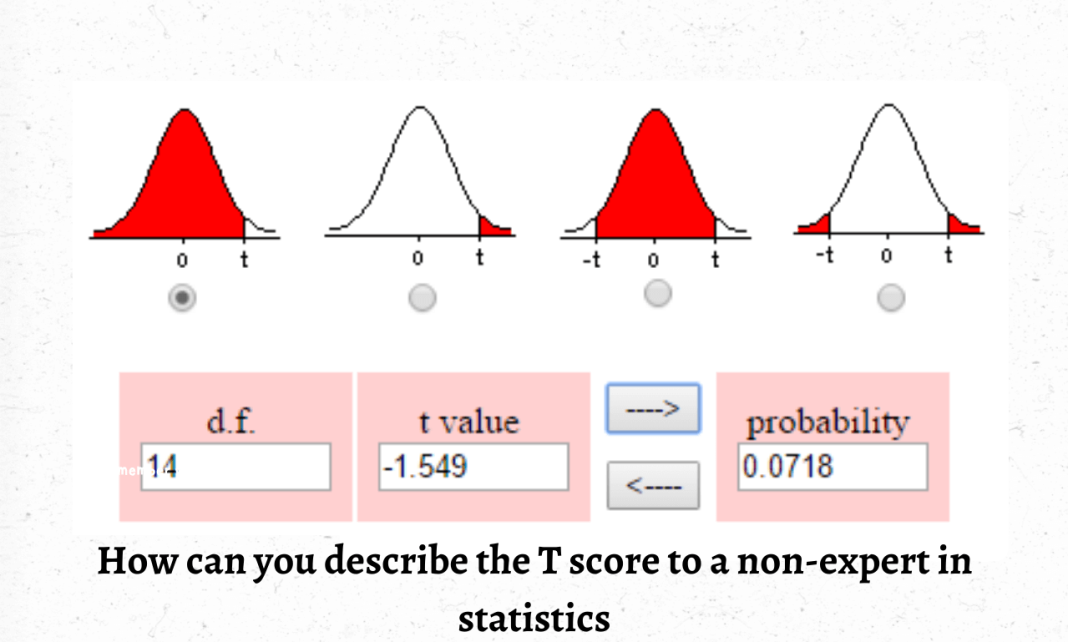
How to Use the T-table to Solve Statistics Problems?
The t-table is designed for solving problems related to the correlation coefficient, which is used to calculate the strength of the relationship between two variables. The t-table helps you find the critical value for any confidence level and degree of freedom. This means that if your experiment has 25 degrees of freedom (df) and a 95% confidence level, then all you need to do is find where there’s a row with 25 df and another with 95%. You’ll see that only one row satisfies both criteria, so this will be your critical value.
How to Read the t-Distribution Table?
The t-distribution is a family of statistical distributions used in hypothesis testing, including the Student’s t-test and the Mann–Whitney U test. It is often called Student’s distribution because it was first introduced by William Sealy Gosset (a Guinness employee), who wrote under the pseudonym Student.
The t-distribution table will tell you how likely your data point would be in either tail of the distribution. For instance, if your data falls into an area where 2% of all possible values lie, then there is only a 2% chance that your data point would have come from that tail.
Final Thoughts
A person’s T-score is an indicator of how much their DNA is similar to the average person’s. It is calculated by determining which alleles are more frequent than others. If a gene has two different alleles, then one of them will be more common than the other. A person with two copies of the less common allele will have a lower score than someone with two copies of the more common allele. The higher your score, the more likely that you may be related to someone else with the same DNA profile.