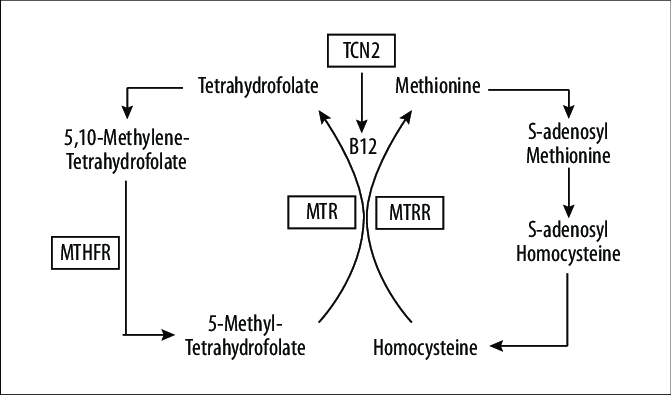
The MTHFR gene directs the production of an enzyme known as methylenetetrahydrofolatereductase. The MTHFR gene instructs your body to produce the MTHFR protein, which aids in the absorption of folate. Folate is required for the production of DNA and the modification of proteins in your body. A gene variation is a difference in the DNA sequence from the anticipated DNA sequence.
Methylation is a chemical process that enables some internal switches (such as physiological receptors) to turn on and off in order to operate properly.
Deficiency:
MTHFR deficiency is an uncommon illness that affects folate and sulfur-containing amino acid metabolism. A mutation at gene location C677T is thought to affect 30 to 40% of the American population. This variation is homozygous in around 25% of Hispanics and 10% to 15% of Caucasians.The average quantity of folate in the blood of persons with the MTHFR677 TT genotype is only slightly lower (approximately 16 percent lower) than people with the MTHFR 677 CC genotype. From population to population, the number of persons with each of these genotypes will vary.
Testing:
This test checks for mutations (differences) in the MTHFR gene. Genes are the basic units of heredity that your mother and father pass on to you.If you think you have an MTHFR mutation, consult with a doctor who can run the right testing to figure out what’s causing your symptoms and rule out alternative possibilities.
Everyone carries two MTHFR genes, one from their mother and the other from their father. One or both of the MTHFR genes can be mutated. MTHFR mutations come in a variety of forms. Two of these mutations, also known as variations, are looked for in an MTHFR test. C677T and A1298C are the two MTHFR variants.
The MTHFR gene aids in the breakdown of a chemical called homocysteine in your body. Homocysteine is an amino acid, which is a sort of molecule that your body needs to produce proteins. Folic acid and other B vitamins normally break down homocysteine and convert it to other amino acids.
During Test:
A health care worker will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm using a small needle. Once the needle is placed, a little quantity of blood will be collected in a test tube or vial.It may hurt a bit as the needle goes in or out. This task usually takes less than five minutes to accomplish.
A health care provider will wipe your baby’s heel with alcohol and puncture it with a little needle for a newborn screening. He will take a few drops of blood and apply a bandage to the wound.
When a baby is 1 to 2 days old, he or she is routinely tested in the hospital where he or she was delivered. If your baby was not born in a hospital or if you left the hospital before the infant could be tested, contact your health care provider as soon as possible to schedule testing.
References:
- Seyoum E, Selhub J. Properties of food folates determined by stability and susceptibility to intestinal pteroylpolyglutamate hydrolase action. J Nutr. 1998;128(11):1956-1960.